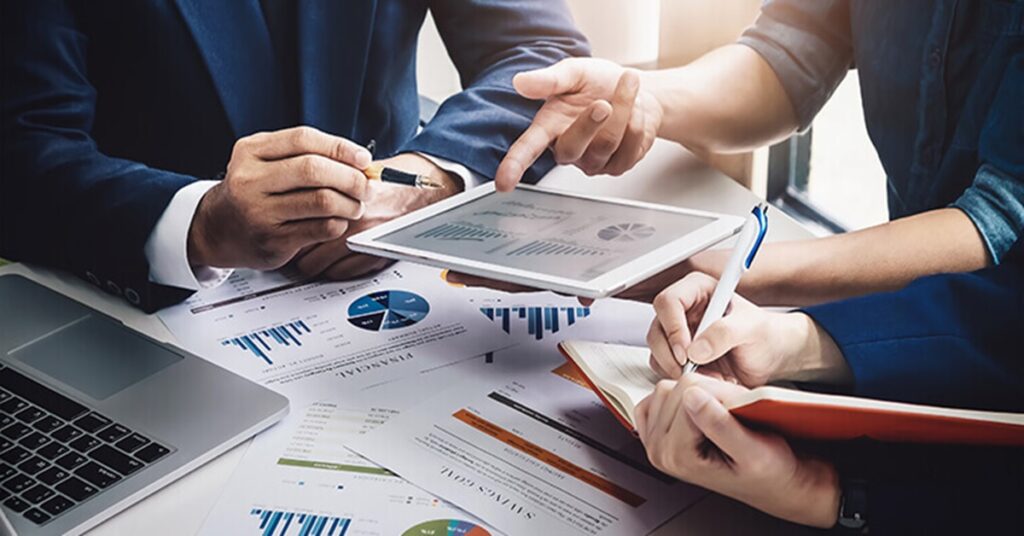
As #Multinationalcompanies (#MNC) increasingly rely on #EmployerofRecord (#EOR) solutions to streamline international workforce expansion, compliance with localized labor statutes becomes a strategic necessity. India’s regulatory framework, particularly in cities like #Delhi, includes distinct rules regarding employee leave and holiday entitlements. For EORs managing employment responsibilities on behalf of MNCs, it is crucial to align with local legal standards to ensure smooth operations and risk mitigation.
1. Statutory Leave Entitlements Under Indian Labor Law
#Indianlaborlaw prescribes several categories of leave, with specifics often varying by state. In Delhi, these are primarily governed by the Delhi Shops and Establishments Act, in addition to applicable central legislation. EOR providers must incorporate these standards into their employment policies to ensure lawful engagement.
a. #EarnedLeave (EL) / #PrivilegedLeave (PL)
Employees earn this leave based on their duration of service—commonly accruing at a rate between 1.25 and 1.75 days per month. In Delhi, workers are entitled to a minimum of 15 days of earned leave per year. Unused days can typically be carried over (up to a limit of 45 days) and may be paid out upon termination, depending on company policy.
b. Casual Leave (CL)
Casual Leave is intended for short and unplanned personal matters. Most organizations in Delhi offer between 7 to 12 days of this leave annually. These days are not carried forward to the next year and are non-encashable.
c. Sick Leave (SL)
Under Delhi’s employment rules, workers are entitled to 12 days of paid sick leave annually. Employers may request a medical certificate for absences that extend beyond a couple of consecutive days.
d. Maternity Leave
The #MaternityBenefit (Amendment) Act, 2017 grants 26 weeks of paid maternity leave to eligible female employees for their first two deliveries. For subsequent births, the entitlement is 12 weeks. Provisions also exist for paid leave in case of miscarriage (6 weeks) and for adopting mothers (12 weeks under certain conditions). EORs are responsible for ensuring these benefits are provided in accordance with applicable laws.
e. Paternity Leave
While there is no statutory #paternityleave in India, many employers in Delhi voluntarily offer 5 to 15 days of paid leave to new fathers. EORs can support clients in implementing such benefits as part of inclusive HR practices.
f. #SpecialLeave Categories
Some companies may offer discretionary leave such as for marriage, bereavement, or education. These are usually governed by internal HR policies or individual employment contracts.
2. Public Holiday Structure in Delhi
Delhi observes a mix of national, gazetted, and religious holidays throughout the year. Employers in India offer 10 to 14 public holidays depending upon the policies and religious observances and are expected to publish an annual list of recognized holidays.
Key statutory holidays include:
- Republic Day (January 26)
- Independence Day (August 15)
- Gandhi Jayanti (October 2)
- Diwali, Holi, Eid, and Christmas, among other regionally significant dates
Organizations may offer #substituteholidays in #india to accommodate religious and cultural diversity, reinforcing their commitment to workforce inclusion.